
Rhinomanometry
Breathing is essential for survival.
A doctor may diagnose you with nasal obstruction based on your subjective account of nasal stuffiness and a limited physical examination demonstrating anatomic restriction of the nasal passages. Rhinomanometry is an objective test that measures the cause of high nasal resistence.
There are many causes of nasal obstruction:
Allergic rhinitis with turbinate hypertrophy
Anatomical nasal septum deviation, bone spur, or conchae bullosa
Sinus or nasal infection
Narrow palate
Four-Phase Rhinomanometry
Four- Phase Rhinomanometry is a non-invasive quantitative measurement of nasal airway function against a pressure gradient from which we can calculate nasal resistance.
Image Source: GM Instruments used, with permission
Four-Phase Rhinomanometry has many clinical uses. As an example, individuals are often recommended nasal surgery without objective confirmation of genuine mechanical obstruction. Measuring nasal obstruction using rhinomanometry before nasal surgery is vital because individuals with preoperative higher nasal resistances are more likely to benefit from the surgery.
Rhinomanometry Uses
Sleep Apnea
Investigate continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) intolerance due to high nasal resistance and assess for CPAP mask interface
OTC Allergy Treatment
Evaluate the decongestive action of antihistamines, corticosteroids, or nasal saline rinse
Rx Allergy Treatment
Evaluate allergy immunotherapy or antibiotic therapy efficacy and response
Children
Evaluate adenoids hypertrophy in children as young as three years old
Pre-Surgery
Individuals with preoperative high nasal resistances are likely to benefit from nasal surgery.
Post-Surgery
Individuals with postoperative low nasal resistances are likely to have benefitted from nasal surgery.
Rhinomanometry Examples
Visual guidance suggests whether airway resistance is within the normal, moderately obstructed, significantly obstructed, or severely obstructed range.
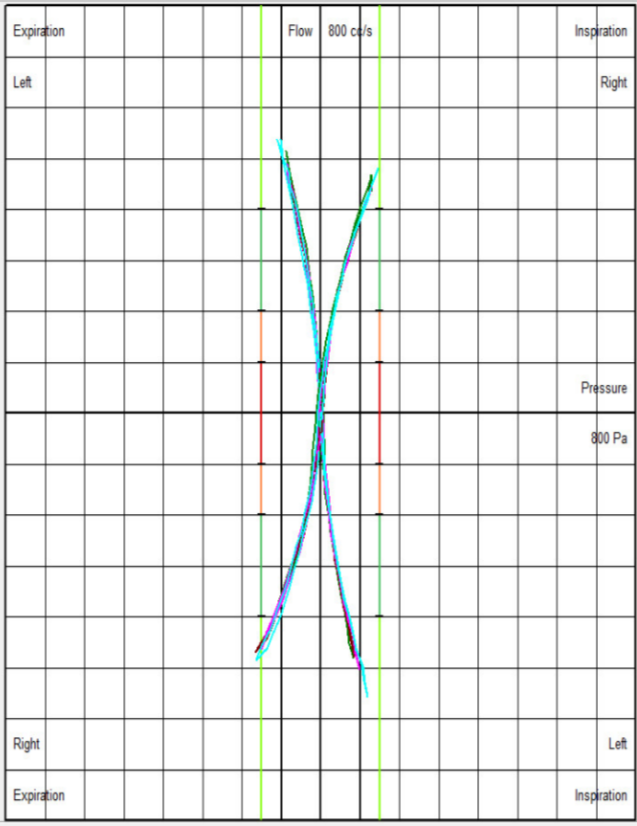
Normal Nasal Resistance
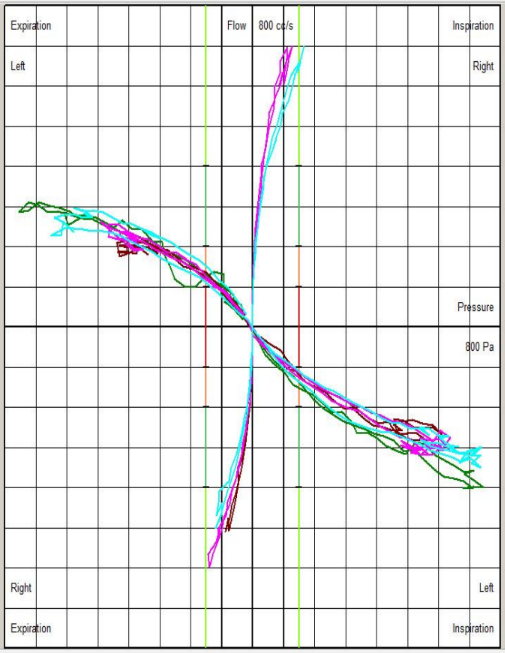
High Left Nasal Resistance
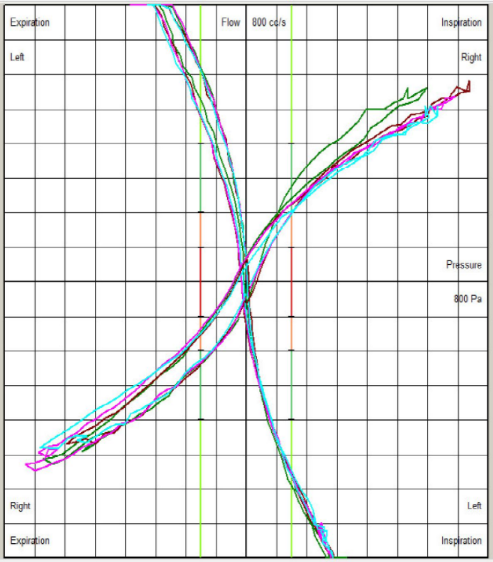
High Right Nasal Resistance
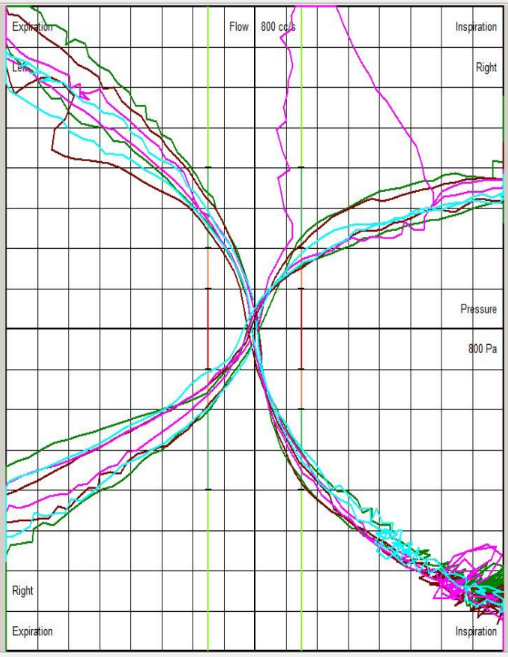
Child with High Left and Right Nasal Resistance

High Right>Left Nasal Resistance


